
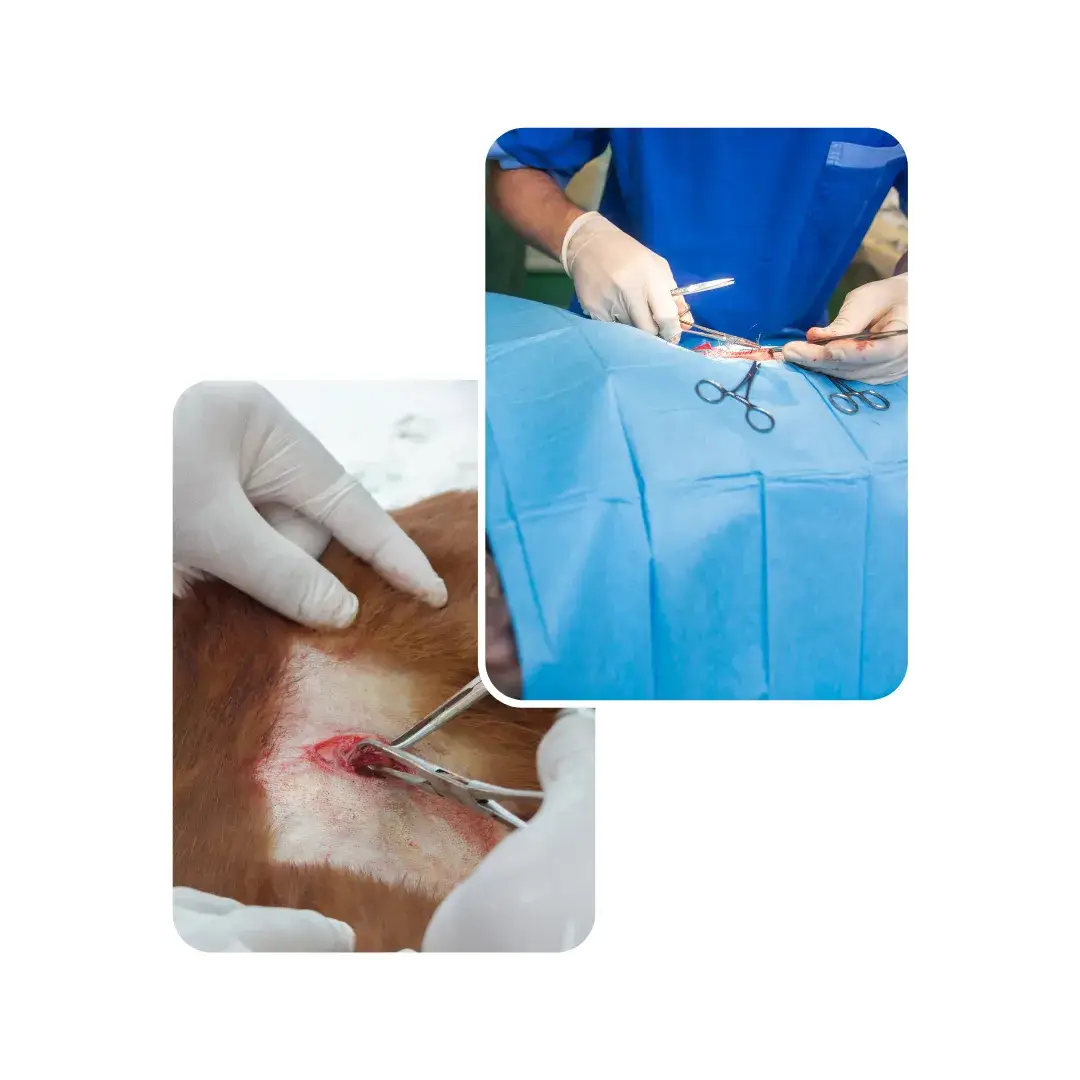
Dog neutering is the removal of reproductive organs—testicles in males and ovaries (sometimes uterus) in females—to prevent health risks and unwanted litters.
Most vets recommend around 6 months of age. Larger breeds may benefit from waiting a little longer, while smaller breeds can be neutered earlier.
Yes, it often reduces aggression, roaming, and marking. Dogs usually become calmer and more focused after surgery.
The surgery is performed under anesthesia, and pain relief is provided afterward. Most dogs recover quickly with minimal discomfort.
Spaying eliminates the risk of pyometra and greatly reduces mammary cancer risk, but other health problems can still occur unrelated to reproduction.
Most dogs recover in 10–14 days. Activity should be limited during this period to avoid complications.
Yes. You can explore more about dog problem and treatment on our dog page to stay informed and prepared.
Your pet deserves expert care – Subscribe now for trusted tips and updates from our pet experts.
